Call the Lab:
+234 810 156 6324
Location:
7 Junvon Close, Ogbaku
Owerri-West LGA, Imo State, NG
Hours: Mon - Fri:
8am - 5pm
Sat: 9am - 3pm | Sun: CLOSED
- Home
- About Us
- Services & Packages
COVID-19 Testing Solutions
Nucleic Acid Amplification SARS Co-V2 and the Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA) methodologies are used in this test. - Research
- News
- Contact Us
Imaging Services
Imaging services are anticipated to become operational in 2026. Junvon Lab is committed to delivering secure and thorough imaging and laboratory services tailored to the needs and preferences of our patients.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are medical diagnostic techniques that create visual representations of the inside of the body. They are crucial for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating various medical conditions. Common imaging modalities include:
1. X-rays
• Purpose: Visualize bones, detect fractures, infections, and lung issues.
• Common Uses: Bone fractures, chest infections (e.g., pneumonia).
• How It Works: Uses low doses of ionizing radiation.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
• Purpose: Provides detailed cross-sectional images.
• Common Uses: Cancer detection, internal injuries, and detailed imaging of bones and organs.
• How It Works: Combines multiple X-ray images using computer processing.
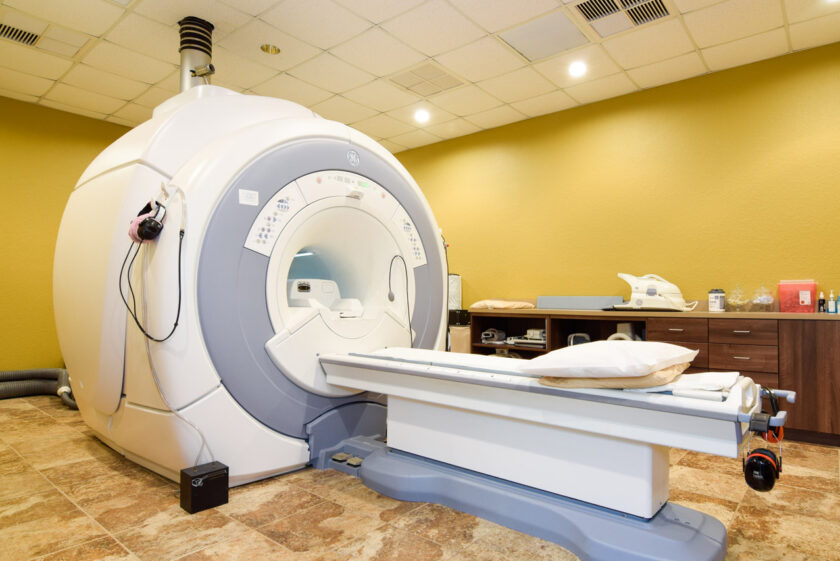
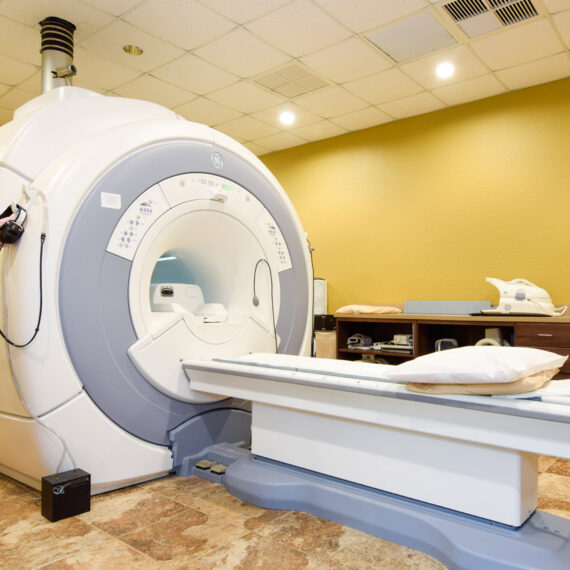
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
• Purpose: Produces detailed images of soft tissues and organs.
• Common Uses: Brain abnormalities, spinal injuries, ligament tears.
• How It Works: Uses powerful magnets and radio waves.
1. X-rays
• Purpose: Visualize bones, detect fractures, infections, and lung issues.
• Common Uses: Bone fractures, chest infections (e.g., pneumonia).
• How It Works: Uses low doses of ionizing radiation.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
• Purpose: Provides detailed cross-sectional images.
• Common Uses: Cancer detection, internal injuries, and detailed imaging of bones and organs.
• How It Works: Combines multiple X-ray images using computer processing.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
• Purpose: Produces detailed images of soft tissues and organs.
• Common Uses: Brain abnormalities, spinal injuries, ligament tears.
• How It Works: Uses powerful magnets and radio waves.
4. Ultrasound
• Purpose: Real-time imaging of internal structures.
• Common Uses: Pregnancy monitoring, gallbladder or thyroid issues.
• How It Works: Uses high-frequency sound waves.
5. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
• Purpose: Visualizes metabolic activity in tissues.
• Common Uses: Cancer diagnosis, neurological disorders.
• How It Works: Uses a small amount of radioactive material.
6. Nuclear Medicine Scans
• Purpose: Examines organ function and structure.
• Common Uses: Thyroid function, bone disorders.
• How It Works: Radioactive tracers injected into the body.
7. Fluoroscopy
• Purpose: Provides real-time moving images.
• Common Uses: GI tract studies, catheter placements.
• How It Works: Continuous X-rays to observe internal motion.
8. Mammography
• Purpose: Detects breast abnormalities.
• Common Uses: Breast cancer screening.
• How It Works: Low-dose X-ray.
9. Interventional Radiology
• Purpose: Uses imaging to guide minimally invasive procedures.
• Common Uses: Biopsies, stent placements.
• How It Works: Real-time imaging guides tools.
10. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
• Purpose: Measures bone density.
• Common Uses: Osteoporosis detection.
• How It Works: Low-dose X-ray.
• Purpose: Real-time imaging of internal structures.
• Common Uses: Pregnancy monitoring, gallbladder or thyroid issues.
• How It Works: Uses high-frequency sound waves.
5. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
• Purpose: Visualizes metabolic activity in tissues.
• Common Uses: Cancer diagnosis, neurological disorders.
• How It Works: Uses a small amount of radioactive material.
6. Nuclear Medicine Scans
• Purpose: Examines organ function and structure.
• Common Uses: Thyroid function, bone disorders.
• How It Works: Radioactive tracers injected into the body.
7. Fluoroscopy
• Purpose: Provides real-time moving images.
• Common Uses: GI tract studies, catheter placements.
• How It Works: Continuous X-rays to observe internal motion.
8. Mammography
• Purpose: Detects breast abnormalities.
• Common Uses: Breast cancer screening.
• How It Works: Low-dose X-ray.
9. Interventional Radiology
• Purpose: Uses imaging to guide minimally invasive procedures.
• Common Uses: Biopsies, stent placements.
• How It Works: Real-time imaging guides tools.
10. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
• Purpose: Measures bone density.
• Common Uses: Osteoporosis detection.
• How It Works: Low-dose X-ray.
Preparing for Test Help Ensure It Go Smoothly.
To reduce your wait time, complete the personal information on the form in advance most routine tests.
Patient Centered Care
We conduct extensive research and analysis to address the inquiries that facilitate progress for individuals in search of solutions.
Quality Improvement
Our team systematically analyzes specimens from over tens of thousands of patients each month and assesses the effectiveness of fifty of the leading hospitals across the nation.
Your Health And Safety Is Important To Us
Schedule An Appointment
Book A Lab Visit
Please feel welcome to contact our friendly reception staff with any general or medical enquiry. Our doctors will receive or return any urgent calls.
With over 90% of health decisions based on diagnostic results, we are committed to being a trusted healthcare partner.
Contact Us
Quick Contact
If you have any questions or need help, feel free to contact with our team.
Send Us Email:
Call Us Today:
© 2024 Junvon Medical Laboratory & Diagnostic Services, All Rights Reserved.

